The purpose of this steel structure installation method statement is to ensure the proper management for the erection work on customer job site safely, correctly and complying with applicable standards.
Applicable international code is “Code of Standard Practices for Steel Building and Bridges section 7 “ issued by American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC).
Additionally during erection period, all requirements of local building regulations, codes and project specifications will be applied.
Roles and Responsibilities
Project Manager
The project manager is in charge of the proper implementation of project requirements, reports to the head office / management, with main responsibilities as below:
Fully responsible for providing the client services, date, reports, other necessary to complete the work within the required safety condition, established cost budget and scheduled completion date.
Plan and conduct all the steel erection related activities to accomplish project timely, with quality, safety as committed.
Reviews and approves official letters, drawing, documents for erection purposes.
Sign-off the submitted detailed installation schedule of the Erector.
Allocate Resources as required and ensure Resources are properly qualified.
Responsible for the client’s payment progress in line of the delivery and installation schedule.
Plan, check and get the design manager sign-off the “Sequence/Method of Erection”
Ensure the adequate plans and actions to solve out all the complaints from the clients/consultants.
Sign-off or get the authorized sign-off for all the non-conformances and implementation of corrective and preventive measures.
Check and record all the required test and inspection documents.
Site Manager
The site manager is fully responsible on behalf of project manager to manage all the activities happening on site, directly reports to the project manager with the main responsibilities as below:
Plan and schedule material, equipment and personnel to perform the work.
Coordinate all installation, delivery, and safety activities at site.
Implements and maintains safe working environment by adhering to correct work practices and health and safety procedures.
Ensures all necessary checks, inspections and tests are carried out and passed before proceeding to next stage of installation, also for all out going and incoming materials from site.
On behalf of the Project manager on site to decide the issues with his assigned authority.
Ensures that the work is carried out on site in accordance to the latest approved drawings and specifications at the time of execution.
Make sure that the steel structure installation work is carried out on site safely.
To monitor all site staff to carry out the project activities and management effectively.
Perform risk assessments as per the site activities and applicable HSE requirements.
Review drawings, specifications and any other applicable codes and standards.
Safety officer Duties
The safety officer shall report to the site manager and safety manager, his main responsibilities include:
Liaise with client safety officer/team to make sure the project safety system is complying with client safety system.
Organize and implement site safety system.
Arrange safety trainings for all staff and workers who are working on steel structure installation project site.
Prepare health and safety risk assessments for all the activities involved.
Analyze all safety information; prepare and maintain the relevant records.
Raise and recognize new risks and hazards that may occur during construction period at the site.
Sets up the filing system and records related to HSE.
Attends all safety meetings arranged by client / consultants.
Erection Superintendent
The erection superintendent shall report to the site manager and project manager, his main responsibilities include:
Monitoring the work and progress of steel structure erection team to make sure the erection work proceeds in line with project schedule, designed quality and approved safety procedures.
Follow the ITP, checklist to carry out site inspection with the erection team to make sure all inspection steps were done adequately.
Liaise closely with the civil contractor to raise objections timely in case any of disagreement is found during steel structure installations and inspections.
Sign off acceptances with client inspector for the work done on site.
Prepare Site daily report for his scope of works.
Erection Team
To report to the erection superintendents, main responsibilities include:
Perform the erection work in line with project schedule, designed quality requirements and approved safety procedures.
Follow strictly all instructions of erection superintendents.
Prepare or arrange adequately, qualified labors, machines, equipment’s to install the steel structure and conduct the erection effectively.
Organize and monitor all team members about every aspect of the work.
Prepare and conduct toolbox meetings, safety training courses to train team members about project safety requirements.
Team Leader (Sub-installer)
Everyday morning, arrange and attend the safety tool box meeting with the safety officer before starting the work.
Organize the work for groups in day to day operations.
Performs 100% pre-checks and pre-inspections before the site supervisor do the official checks and inspections.
Material Controller (Sub-installer)
Responsible for the storage of the materials.
Controls incoming and out going materials from store.
Sequence of Work for Steel Structure Installation
Job Site Planning & Preparation
Make sure there is space and firmed pathway for truck delivery, crane truck involved in erection operation.
The suitable truck & crane capacity must be clarified (and listed in the equipment register).
Survey the wind direction to have plan for roof material storage and installation direction.
Decide the plan for unloading and material storage.
Choose a firm and dry location.
Materials shall be stored in designated areas for each building and clearly identified for their location in that area.
Make sure that materials supply and storage schedule is appropriate and not conflicting with the installation schedule and other sub-contractors’ schedules.
Register the available power & water supply source locations at the site.
Make sure there is a safe method to lead the supply to the working area.
Receiving of Material at Site
All delivery to site shall be informed by production people to the site manager 24 hours earlier to have plan for unloading.
A delivery note is always enclosed with the supplied materials to clarify name of project, location, building number, type of materials, quantity, date of delivery, etc.
Upon arrival of materials at the storage yard, the material controller will match delivery notes and shall verify the consignment.
The material controller, then, reports to the site supervisor the received material list and quality condition.
Unloading can be done manually or with cranes.
A spreader should be used for lifting long components.
Lifting nylon or cloth belts with suitable SWL shall be used for unloading the materials to minimize the damage.
Be sure to hook belts to component with the right number of points and position so that the load of component itself is not damaged or broken.
Always attach a tag line to the lifting component.
All materials receipt at site shall be visually inspected by site supervisor for any damage.
Remedial works to the damage shall be taken immediately, if possible, to avoid any delay to erection.
Sequence of Erection
Structural frames and other parts of the building can be erected in various ways which will depend on the following key factors:
The type of structures such as: small clear span, large clear span, low rise building, high building, taper I structure, open-web structure, etc.
Availability of equipment such as cranes, winch, manual lift, etc.
The site conditions.
Experience level of the erectors.
The individual job conditions.
Sequence/method of erection shall be studied and planned so that execution can be carried out in a safe, economical and efficient manner.
There are certain erection practices which are in general use and have proven sound over the years.
Below are typical instruction applied for a single/double span structure.
UNLOADING
Materials are shipped to job site separately or on the skid put in container.
They are unloaded by crane or worker manually depending upon the material size, weight and properties etc.
Average load of trucks carried materials is about 40 ton, this load is also the safe working load of crane of 20 tons capacity.
Therefore, the temporary road in the job site must be prepared properly for crane and trucks working.
Before unloading materials out of trucks or containers, it is required to take pictures of real material status delivered to job site.
MATERIAL ARRANGEMENT
To avoid materials being moved so much on jobsite that might cause unexpected damages of paint, shapes, when material delivered to job site, they must be unloaded and arranged close to the designated erection point.
The materials shall be stacked in locations according to the building/areas, should be near to the lifting position adjacent to the area to be erected. This is to facilitate the sorting and delivery during the erection.
Depending upon the conditions of each job site, the material arrangement plan may be different but generally, materials will be arranged as following principle to ease moving, combination and erection later.
Members should be check marked as packing list enclosed before unloading for best unloaded positions.
Columns should be arranged closed to their anchor bolt position.
Rafter members should be arranged to ensure easy assembly, movement.
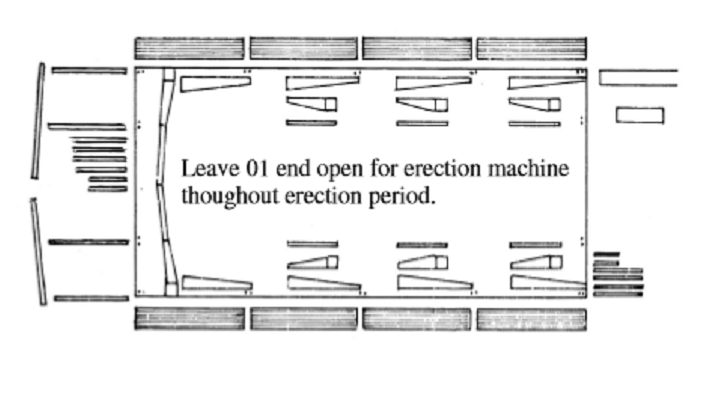
Girts, purlins, eave struts and bracing are divided according to the requirements of each bay.
Nested parts (purlins, girts etc.) should be separated and blocked to allow drainage of collected moisture to prevent rusting, prior to erection.
End wall material is laid out for each end.
Small components (nuts, bolts, clips, fasteners etc.) are stored in a given areas convenient to all parts of the building.
Wall, roof paneling and other components which will not be used in the initial stage of erecting the steel structure, are placed to the outside of the work area and properly stored and protected from the weather.
Insulation should not be stored on the edge of the roll as this will damage the edges.
PROTECTION & STORAGE OF MATERIALS AT SITE
For the purpose of preventing and protecting material damages during storage out of environmental factors such as storm water and dust which cause rust / stain, include below tasks:
Choose firm and dry area for storage.
Material shall be stored above ground level with timber packing.
The materials or components or members shall be stored separately, above ground on timber dunnage.
They shall not be stacked directly on top of each other but must be separated by 50mm thick timber, and shall not stack in contact with other steel member but must be separated by a minimum 250mm gap.
Particular care shall be taken to stiffen free ends at 200mm distance from ends, prevent permanent distortion.
The materials should be placed in minimum 5% slope to avoid water pond.
Materials shall be kept free from dirt, grease, and other foreign materials and shall be protected from road splash.
Never step on the materials.
All bolts, nuts, washers, screws, small plates and articles generally shall be suitably packed and identified.
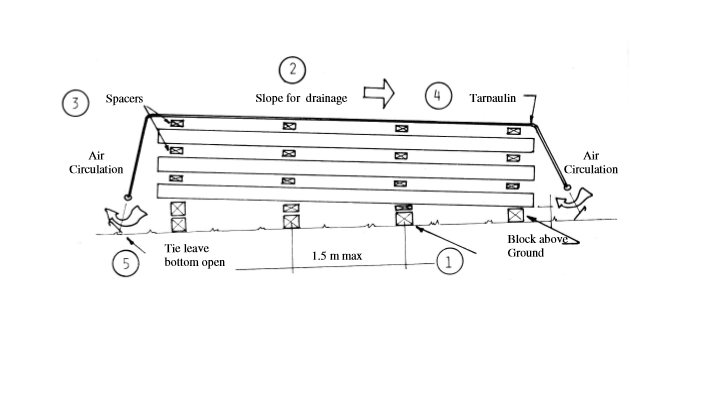
Block above ground to keep water out.
Slope bundles for drainage.
Stack sheeting with spacers between bundles.
Cover with canvas tarpaulin to protect from rain.
Tie down cover ends away from stack to permit air circulation. Do not wrap under or restrict air movement.
IMPORTANT!
Do not use plastic sheeting as a cover because it will promote moisture.
Sheeting, wire mesh, insulation should be installed right after delivering to job site, if not must be kept indoors.
Where indoor storage is not possible, the above procedure must be applied.
ERECTION GENERAL PRINCIPLE
Do not conduct erection without latest erection drawings issued for steel structure installation and erection.
Adequately do the bracing before releasing lifting equipment’s or temporarily stop working.
First braced bay must be completed with rod bracings, eave strut, purlins, girts and flange bracing as well as all connection bolts must be tightened to ensure the stable placement for next structure connections.
Only erect rafter after all connection bolts are tightened, rafter is cleaned and rafter is signed off.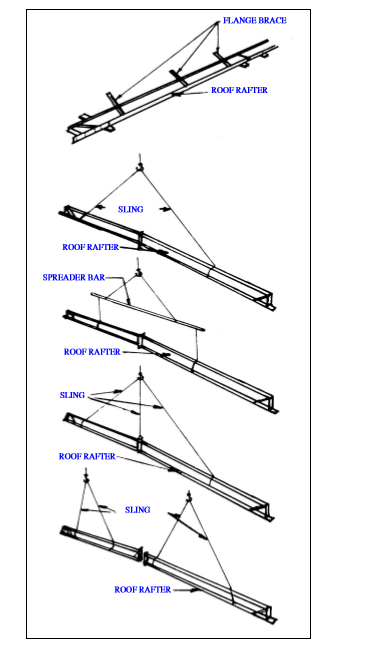
All connection joints must be completed with bolt tightening before releasing lifting equipment.
MEMBER ASSEMBLANCE
All assembled members should be bristled by timber bar, cleaned, painted touch up.
Flange braces should be installed to rafter members then.
Connection bolts must be tightened, and checked on the ground by TURN OF NUT or Torque Wrench method.
MAIN FRAME ERECTION
Repeat procedure of erection columns, rafters to complete the frames.
COLUMN ERECTION:
Preparation
Column materials are arranged closed to designated installation area.
Columns materials need to be cleaned, paint touching up and assembled before erection.
Attach driven rope to column.
Check level and position of level nuts and anchor bolts with design.
Check at least 03 temporary anchor points to ensure safe anchor points for column after erection.
These points should be adjacent to the casted concrete structures (stump, ground beam) where temporary cable can be tied to.
In case of no anchor point available, steel members that are not yet in use can be temporary applied for temporary anchor point.
Temporary anchor points should be arranged out of working area to avoid hanging materials caught by temporary cable, this can cause collapse to erected structures.
Check lifting weight, crane position with capacity of applied crane base on crane specification issued by manufacturer.
Erection
Lift column and move slightly to designated position.
Slightly down column on casted anchor bolts.
Tighten anchor bolts nut after column in right position.
Temporary cables will be applied to keep column in position.
RAFTER ERECTION:
Preparation to be done as per the procedure shown above.
Install static line poles, static line and driven ropes into assembled rafter.
Make sure all mentioned equipment is checked strictly.
Scaffolding should be prepared for workers to perform rafter to rafter and rafter to column connection safely.
Check at least 03 temporary anchor points to ensure safe anchor points for column after erection.
These points should be adjacent on the casted concrete structures (stump, ground beam) where temporary cable can be tied to.
In case of no anchor point available, steel members that are not yet in use can be temporary applied for temporary anchor point.
Temporary anchor points should be arranged out of working area to avoid hanging materials can be caught by temporary cable, this can cause collapse to erected structures.
Check lifting weight, crane position with capacity of applied crane base on crane specification issued by manufacturer

Rafter Erection
Lift the rafter slightly up.
Workers on the ground will drive rafter to right position in coordination with the crane operator.
Workers standing on scaffolding will adjust rafter for bolting.
After rafter is connected to right positions, workers will follow rafter with PPE attached to static lines to install temporary purlins, rod bracings, flange braces.
Crane is only released when all connection bolts are tightened, temporary bracings, bracing purlins, flange braces are installed adequately.
Make sure there are at least 02 braced purlins installed for each rafter portion when there are more than 01 rafter portions.
Temporary cables will be applied during mainframe erection period, up to certain case, the number of these cables can be deducted to avoid blocking the steel structure erection process.
STEEL STRCUTRE INSTALLATION / ERECTION SEQUENCE
Braced bay erection
Braced bay must be erected in priority.
After completion of the 02 frames of braced bay, all components such as brace rod, flange brace etc. of this bay must be completed as per the design, to set up the stable place for next frames.
Temporary bracing should be applied for this bay during erection for safety.
Braced bay frames must be temporarily aligned before installation of purlins, bracings may get difficulties if conducting alignment for remained frames after that.
After completion of frames alignment, inspection request for approval of client should be raised and approved before starting the sheeting works.
Alignment method is given in below sections.
Filling grouting should be done before sheeting.
Remaining frames erection
Proceed with the erection of the remaining frames and bearing end frames.
In each braced bay shown on the erection drawings, repeat above steps before proceeding with the erection of additional bays.
Eave struts and peak purlins may be installed in intermediate bays between braced bays to stabilize frames, however, do not start more work that can not be completed in a work day to ensure all structural framing is completed in those bays before leaving the site at the end of the day.
As erection progresses, each braced bay must be fully completed as outlined in step above before proceeding with the erection of additional bays.
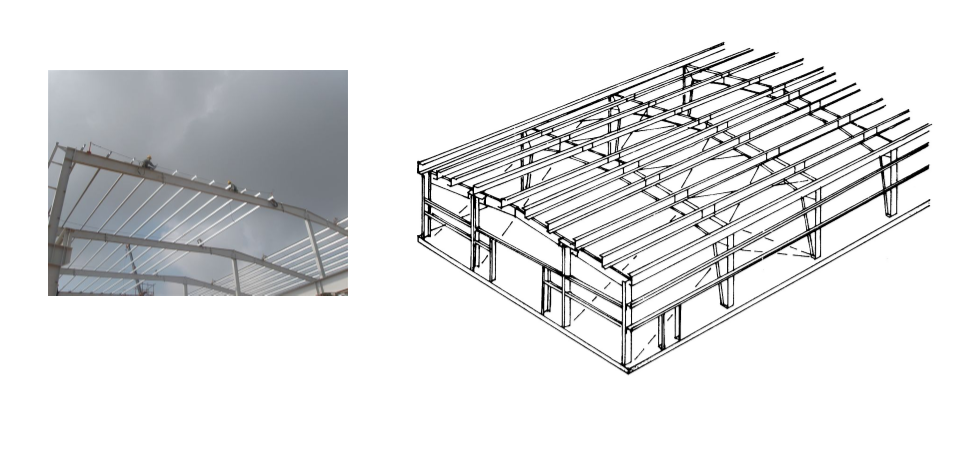
Finish Frames & Accessories
Complete erection of main and secondary framing.
Upon completion of all secondary framing in the braced bay, plumbing and squaring the braced bay, installing secondary framing in the end bay, paneling may commence and be worked in conjunction with the completion of the balance of the secondary framing.
This could save time on larger buildings if separate sheeting crews are used.
When the building reaches this stage of erection, sheeting should proceed immediately.
The structure without sheeting should not be left standing for prolonged periods of time without taking proper precautions (temporary bracing, blocking etc.) to prevent wind damage especially to purlins and girts due to excessive vibration they are exposed to in the unsheeted condition.
SHEETING PROCEDURE
Preparation
Before sheeting, all the tasks below must be completed:
The period completion report of mainframes must be approved and signed off by client/consultant.
All column baseplates gaps must be filled with grouting to make it strong enough for bearing the supports / loads.
Frames must be completed with respect to painting touch up.
Safety net is installed below right after completion of all purlins.
Complete Sag Rod
After installation of safety net, workers will push the channels, which put across purlins along purlins for sag rod installation.
PPE will be attached to purlins for safety.
Install wire mesh, NFR and insulation sheets
They all shipped to job site in shape of coils.
Because of light weight, these are lifted onto the roof by manpower and installed by lying from the ridge of the roof to the eaves.
Insulation sheet will be laid on the strip of installed wire mesh or NFR.
NFR is installed by sticking on 02 size tape stuck on to the top face of purlins.
Roof sheets must be installed right after completing each strip of insulation sheet to avoid the insulation sheet being damaged by rain or wind.
Lifting roof sheet:
Roof sheet will be lifted on to the roof by crane or manually by workers.
(a) Lifting by crane
Roof sheets will be piled up to set of 10 sheets then being tied together by soft ropes at the space of maximum 4 meter.
With roof sheet length <25m , 01 crane is applied.
With roof sheet length >25m , 02 cranes are applied.
Suitable spreader bars will be applied for lifting purpose.
The lifted roof sheets will be arranged to adjacent bays, pilled, and tied carefully to purlins until being installed.
(b) Lifting manually by workers
Roof sheet will be moved to right position and pulled sheet by sheet on to the roof by workers sitting on the rafter with PPE attached to static lines.
Roof sheets lifted on to the roof will be arranged to adjacent bays, pilled and tied safely to purlins before installation.
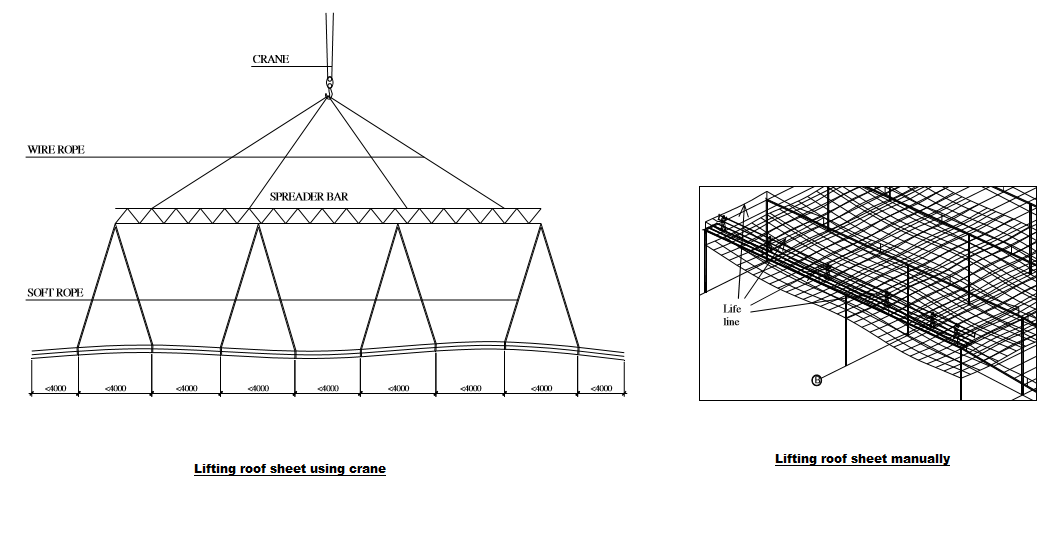
Installation Methodology of Roof Sheets
Roof sheets which are waiting for installation will be tied to purlins by ropes.
Before installing roof sheet, safety net to be installed for safety purposes.
Roof sheet must be installed by only 01 way from predetermined end gable of the building, this end gable should be closed to the Rolling machine of position of fabricated roof sheet to avoid moving too much, this might cause damages to them.
Roof sheet will be installed one by one manually by workers.
KV35, KR32 roof sheet will be attached to purlins by screws while KSS600 by clips and seaming after completing checking.
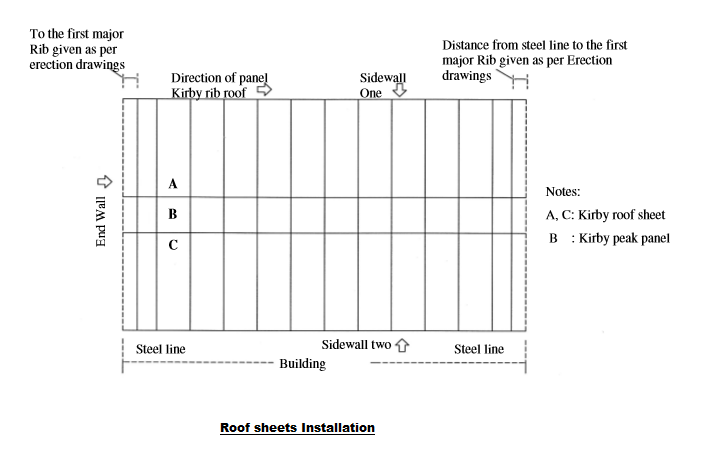
All the accessories related to installation sheeting and the order of installation will be complied as per the sketch given below.
Locate the center of the first major rib exactly over steel line or as indicated in the erection drawing attach panels (A) and (C) and then attach peak panel (B).
Each side of Kirby panel and the Kirby peak panel must be run in conjunction with each other to ensure correct alignment.
Refer to other sections of this procedure for details relating to eave alignment of roof panels, sealer application and fastener types.
All damaged paint finishes are to be retouched to prevent rusting.
In the event a screw is installed in the wrong location or should a screw break during the driving process, remove the screw and install one of the larger diameters to prevent leaking.
Concentrated heavy loads (personnel or material) occurring on the roof during construction shall be distributed uniformly over a large area in such a manner as to prevent damage to building components.
All metal shavings occurring as a result of drilling operations on the roof are to be removing in such a manner as to prevent damage or staining of roof finish.
SWEEP ALL DRILL SHAVINGS FROM PANELS AND TRIM DAILY, OR HUMIDITY AND RAIN WILL CAUSE THE SHAVINGS TO RUST OVERNIGHT AND STAIN THE MATERIAL!
Walking on the Roof
When walking parallel to the ridge line, step directly over a purblind.
NOT STEP ON A PANEL MAJOR RIB and DO NOT WALK ON ANY PANEL THAT HAS NOT BEEN PROPERLY SECURED TO THE STRUCTURE.
When walking up-slope or down-slope, step to either side of a major rib.
A life line is to be installed along to sheeting way for worker hooking their PPE to life line for roof sheeting.
After completion of roof sheet, life lines will be dismantled and re fixed to 2 ends to major ribs of roof.
INSTALLATION OF CLADDING
Preparation
Wall sheets are fabricated in plant and shipped to job site in packages.
Before installing sheeting, make sure all girts and sag rods installation is completed.
A set on scaffolding will be used for cladding, a pulley will be installed on scaffolding, and this allows pulling wall sheet safely by people on the ground or on the scaffolding.
Wall panel will be moved to their position along the wall to install.
Lifting wall sheet:
Drill a hole with dia. of 12mm at the middle of the wall panel 150mm far from the top for hooking wire rope to the wall panel.
Lift up and adjust panel to right position before attaching to the girt.
Workers working on scaffolding must wear PPE attached to scaffolding.
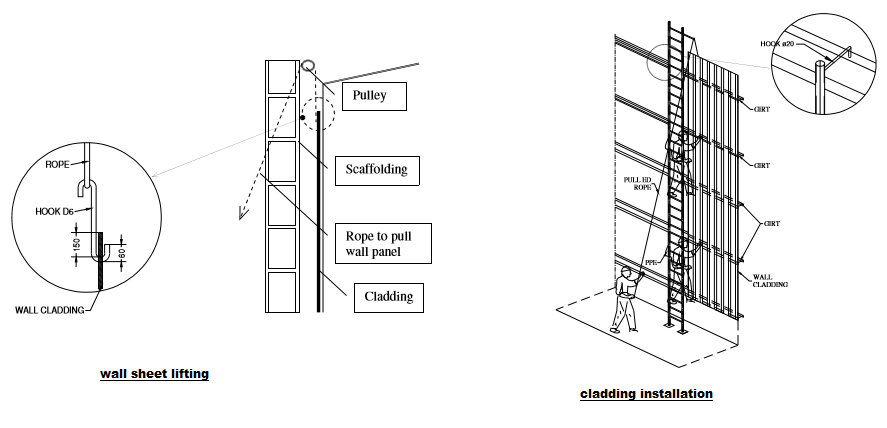
Installation of Cladding
A steel ladder as sketch will be used for girt installation.
Worker stand on ladder which stand on ground and attached to girts to avoid fall down, will fix cladding to the girts.
Need to install a thread to make sure the screws are installed straight.
Platform for cladding must be flat and strong enough.
In case this requirement is not met, supervisor have to contact to client immediately to solve by issuing the RFI.
Health and Safety Requirements
The workers working on job site must be equipped with minimum PPE as below:
Safety Helmet
Safety shoes, Soft shoes when working on the roof otherwise safety shoe all the time
Full body safety harness with 01 or 02 hooks, for all workers working at heights and must be attached to static line at all times.
High visibility vest
Safety gloves
Safety Goggles / Face shield (for grinding, cutting )
Ear Protection (working near generator, or high noise level areas)
Work permit card to be worn by all personal working on site.
Visitor cards for visitors.
All erector workers and sub contractors must attend induction training prior to commencing work at site.
A toolbox meeting must be held at the start of every shift. The purpose of the toolbox meeting is to communicate the work to be done during that shift, the hazards involved and the control measures in place to manage the risk.
The other special requirements such as Safety glass, ear muffler etc. will follow with site requirement individually.
Static lines should be used to ensure safe anchor points for safety harnesses.
Workers must be warned about opened holes on the roof. Any of opened holes with out cover must be protected carefully.
Workers are not allowed go up and down by columns or other structures, ladder and or scaffolding must be used for this purpose.
Safety nets shall be installed for roofing , and being hung far enough above objects below so that the net does not contact lower objects.
Safe access must be provided to the roof at all times.
The most common method for roof access is by using scaffold specifically installed for this purpose.
